dBm - Decibels in relation to a milliwatt (usually -30 to -100)
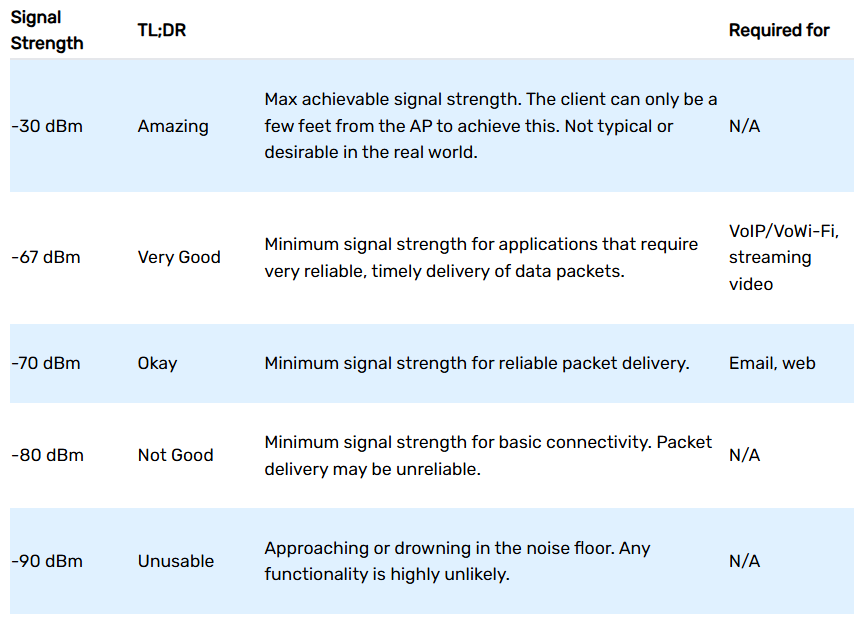
Wi-Fi signal strength is measured in dBm, with values ranging from -30 (excellent) to -90 (unusable). The closer to zero, the stronger the signal.
| Signal Strength (dBm) | Quality | Typical Use |
|---------------------------|----------------------------------|------------------------------------------------------|
| -30 dBm | Maximum strength | Standing next to the router |
| -50 dBm | Excellent | Ideal for all applications |
| -60 dBm | Good | Reliable for most tasks |
| -67 dBm | Minimum for reliable streaming | VoIP, video calls, HD streaming |
| -70 dBm | Fair | Web browsing, email |
| -80 dBm | Poor | Barely usable; may connect but unreliable |
| -90 dBm | Unusable | Likely no connection or very unstable |
Key points to remember:
- dBm values are negative, and higher numbers (closer to 0) mean stronger signals.
- RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) is another metric used, but it’s not standardized across devices. It’s often converted to dBm for consistency.
- Signal strength needs vary by application: VoIP and video conferencing require stronger signals than basic web browsing.

